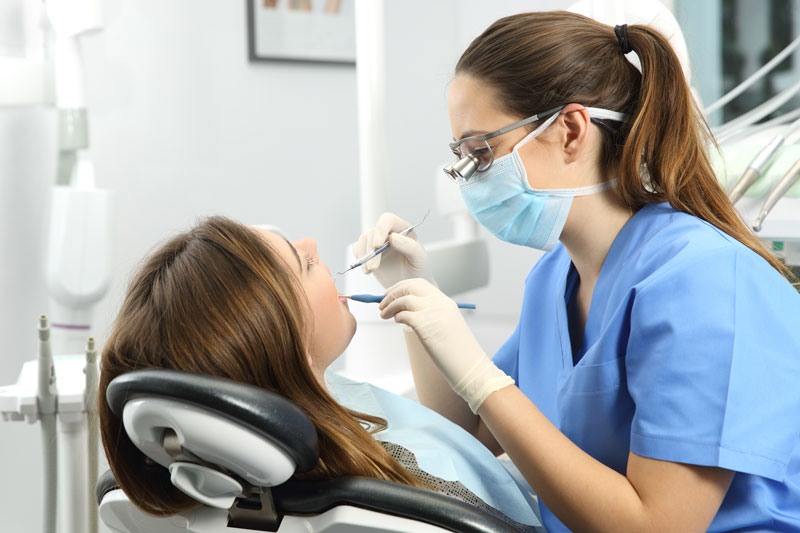
When people have had one or more missing teeth for a long period of time, they could have bone loss in their jaw where their missing teeth were. Luckily, at a skilled and trusted periodontist’s practice, people can treat their bone loss with bone grafting in Columbia, MD. What could happen, however, if people don’t treat their bone loss with bone grafting.
There are a number of things that could happen if people don’t treat their bone loss with bone grafting. Curious to learn about what exactly could happen if people don’t treat their bone loss with grafting? Continue reading to learn about the things that could happen if people don’t treat their bone loss with bone grafting.
The Things That Happen If People Don’t Treat Their Bone Loss With Bone Grafting In Columbia, MD
If bone loss, in areas of a person’s jaw where they have lost a tooth or teeth, is not treated with bone grafting, there are numerous things that could happen. The following are the specific things that could happen if people don’t treat their bone loss with bone grafting.
Wrinkles Around The Mouth:
Bone loss in the jaw can significantly affect a person’s facial structure, particularly around the mouth area where it can lead to increased wrinkling. This happens because the jawbone supports facial tissues. When the bone starts to deteriorate, there’s less structural support for the skin, causing it to sag, fold, and form wrinkles.
Wrinkles are particularly noticeable around the mouth, where the movement and flexibility of skin are crucial for expressions. Bone grafting helps in maintaining the jaw’s shape and density, giving the necessary support to facial tissues and potentially reducing the formation of wrinkles around the mouth.
Shifting Remaining Teeth:
Without using bone grafting to treat bone loss, remaining teeth can begin to shift or drift into the spaces left by missing teeth. Shifting teeth happens as the jawbone loses its density and the natural equilibrium within the mouth is disturbed. Teeth rely on the support of the jawbone and one another to maintain their position. When the bone deteriorates, teeth adjacent to the gap lack the necessary stability to remain in place and may lean or move into the empty tooth socket.
When teeth shift, it can lead to dental misalignment, impacting the person’s bite and causing them chewing and speaking issues. Having shifting teeth can make teeth cleaning more challenging, increasing the risk of plaque build-up, gum disease, and further tooth loss.
Unable To Maintain A Normal Diet:
If bone loss in the jaw is not addressed through treatments like bone grafting, people may find it increasingly difficult to maintain a normal diet. This is because the structural integrity of the jaw is compromised with bone loss, making it problematic for people to chew and bite various types of foods, especially those that are harder or require more effort to break down.
People with bone loss may then favor softer, more processed foods that require less chewing force, potentially leading to nutritional deficiencies and a less balanced diet. Over time, this change in dietary habits can affect a person’s overall health.
Premature Facial Aging:
Premature facial aging is a notable consequence of untreated bone loss in the jaw. The jawbone’s primary role in a person’s facial structure and support means that any deterioration in the jaw, due to bone loss, directly affects the appearance of their face. Without the firm support of a healthy jawbone, facial muscles and skin lose their underlying structure, leading to their jawline and cheeks sagging.
This sagging can significantly age a person’s appearance, as the skin no longer has a taut, youthful contour. Bone grafting helps prevent this by replenishing the lost bone so that the shape and strength of the patient’s jawbone is maintained.
Resorbed Jawbone:
A resorbed jawbone is another significant risk of not treating bone loss through bone grafting. The term “resorption” refers to the process where the body breaks down and absorbs the bone tissue, leading to a decrease in bone mass and density. This phenomenon is particularly concerning in the jaw, where the absence of tooth roots (due to tooth loss) means that there’s no stimulation for the jawbone.
Normally, tooth roots help maintain bone density through the pressures and stimuli of chewing and biting. Without this stimulation, the jawbone begins to deteriorate, a process that accelerates with untreated bone loss. Over time, this can lead to a person having a resorbed jawbone, which not only affects their facial structure and aesthetics, it also affects their future dental procedures, like dental implants.
Have Trouble Speaking Clearly:
Difficulty in speaking clearly is another significant consequence of untreated bone loss that can be treated with bone grafting. When the jawbone deteriorates due to bone loss, it can lead to the shifting and misalignment of teeth This misalignment affects how the teeth come together during speech, potentially altering the way people pronounce certain sounds and making speech less clear.
The loss of teeth can also directly impact one’s ability to pronounce words correctly, as teeth play a crucial role in speech by controlling airflow and helping to form specific sounds. Bone grafting helps prevent these issues by preserving the jawbone’s structure, supporting the proper alignment of the patient’s teeth.
Ill Fitting Dentures:
Ill-fitting dentures are a common issue for people suffering from untreated bone loss, as the underlying jawbone deteriorates and changes shape. Dentures are designed to fit snugly against the jaw, relying on the bone’s shape for a stable and comfortable fit.
Bone loss, however, can lead to the jawbone shrinking or resorbing, causing the dentures to become loose and less secure over time. Ill-fitting dentures not only cause discomfort and difficulty eating or speaking, it can also lead to people getting sores and infections from the constant friction and movement of the dentures against the gums.
Thinning Lips:
Thinning lips are a direct consequence of untreated bone loss in the jaw, a condition that increasingly becomes evident as the support structure of the face erodes. The jawbone, being crucial in providing the foundation for facial aesthetics, supports the teeth and the surrounding soft tissues, including the lips.
When bone grafting is not utilized to counteract bone loss, the diminishing jawbone has less structural support, causing the lips to retract and appear thinner.
This occurs because bone loss reduces the height and width of the jawbone, which in turn leads to a decrease in the vertical support for the lips. Without getting their bone loss treated with bone grafting, people may notice a significant alteration in their lip fullness and the overall appearance of their mouth, making them look older than they really are.
TMJ Disorder:
TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorder is a potential complication that may arise from untreated bone loss in the jaw, if it is not treated with bone grafting. The TMJ is responsible for connecting the jawbone to the skull, facilitating movements required for chewing, speaking, and yawning. When bone loss occurs, it can alter the jaw’s alignment and compromise the balance of muscle and bone function surrounding the TMJ.
This imbalance puts undue stress on the joint, leading to a range of symptoms including pain, discomfort, popping or clicking sounds, and even limitations in jaw movement. Bone grafting can help prevent the onset of TMJ disorder by restoring the normal structure of the patient’s jawbone, maintaining the proper function of the temporomandibular joint and minimizing the risk of developing TMJ complications.
The Need For More Extensive Dental Procedures:
Untreated bone loss in the jaw not only compromises dental health and facial aesthetics, it also necessitates more extensive and complex dental procedures in the future. When bone loss progresses without intervention, the diminished jawbone integrity makes it increasingly difficult to perform routine dental restorations, such as the placement of dental implants or dental bridges.
These dental solutions require a certain level of bone density and volume for successful implantation and long-term stability. Without adequate bone structure, patients might need to undergo additional, more invasive procedures like extensive bone grafting or even reconstructive surgery to rebuild the jawbone before any restorative work can be considered.
This not only significantly increases treatment time and cost, but also the patient’s discomfort and recovery period. Early intervention of bone loss with bone grafting, therefore, is crucial in preventing the need for these more complicated and burdensome dental procedures, thereby preserving the patient’s oral health and quality of life.
See Us Now So We Can Treat Your Bone Loss With Bone Grafting
Don’t hesitate to get the smile of your dreams with our bone grating procedures. Why wait to transform your smile with us? Get in contact with Dr. Sandu Jose, Dr. Keyla Torres, Dr. Andrew Chon, and our exceptional team at our Columbia Center for Implants & Periodontics practice to schedule an appointment today!